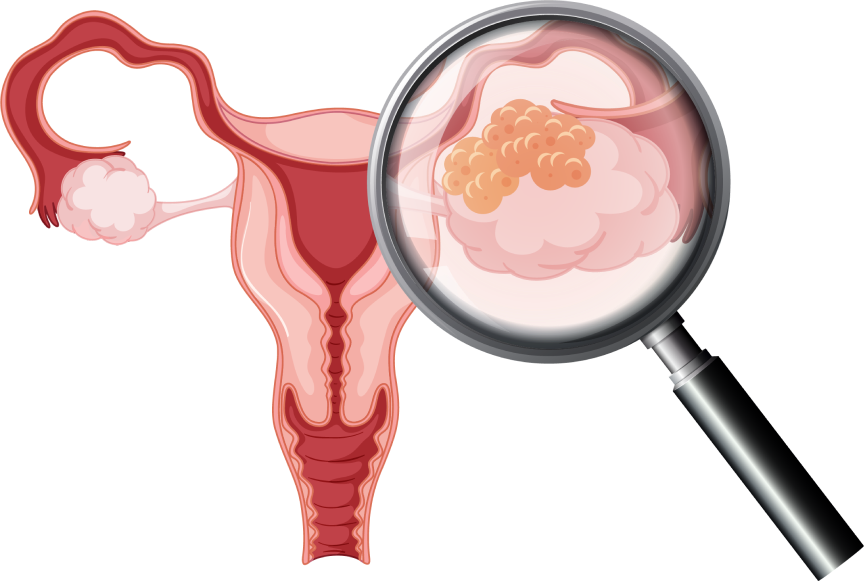
While the exact triggers of ovarian cancer are intricate and multifaceted, several risk factors have been identified:
Genetic Inclination:
Inherited mutations in genes such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 substantially elevate the
risk of ovarian cancer development.
Age Factor:
The likelihood of ovarian cancer increases with age, particularly after menopause.
Reproductive History:
Factors like never having been pregnant, starting menstruation early, or experiencing
late menopause can contribute to heightened risk.
Hormone Therapy:
Prolonged use of estrogen without progesterone in hormone replacement therapy may amplify the risk.
Arming oneself with knowledge and embracing proactive strategies can be instrumental
in preventing ovarian cancer:
Genetic Counseling:
For individuals with a family history of ovarian
or breast cancer, genetic counselling and testing for BRCA mutations are advisable.
Hormonal Balance:
Consider long-term use of oral contraceptives, as
evidence suggests they may reduce the risk of ovarian cancer.
Healthy Lifestyle:
Maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular
physical activity, and managing body weight contribute positively.
Routine Check-ups:
Regular gynaecological check-ups and pelvic examinations
aid in monitoring reproductive health and detecting potential issues.
Symptom Vigilance:
Being aware of symptoms such as persistent bloating,
abdominal discomfort, changes in bowel habits, and frequent urination can prompt timely medical attention.
Clinical Trial Information
Aliquam lacinia elementum enim, et feugiat purus lobortis et. Duis a odio mauris.
Suspendisse consectetur sapien vitae odio ultrices tempus. Integer quam metus,
posuere hendrerit iaculis eget, ornare sed lorem. Duis eu fermentum lacus. Maecenas
faucibus libero mattis risus interdum, ac molestie urna tincidunt. In elit ex,
elementum sed nulla aliquet, aliquam euismod ipsum. Nulla facilisi. Ut consequat sit
amet lacus quis iaculis. Praesent ac semper risus, id semper sem. Sed non tortor et
lectus vestibulum consectetur. Fusce tempor non metus sit amet faucibus. Morbi nulla
tortor, tincidunt interdum posuere nec, posuere id sem. Praesent id mattis leo,
tempus pretium diam. Cras et velit ac tellus egestas sollicitudin tempor a ante. In
gravida, purus quis pulvinar gravida, sapien nisi rutrum velit, vel semper orci
lectus vel leo.